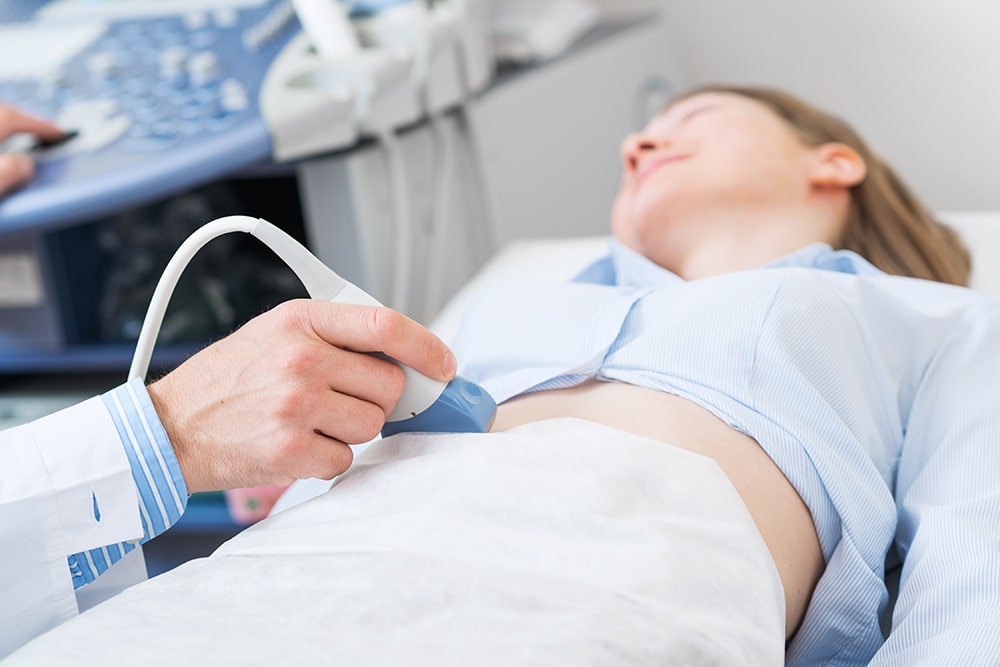
Pelvic ultrasound is one of the most common gynaecological examination procedures. By performing pelvic ultrasound, gynaecologists could evaluate condition of uterus and ovaries, such as shape, size, endometrial thickness, polyps etc. and assess whether any pathological changes exist.
Common pathological changes identified :
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial polyps
- Uterine fibroids
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial cancer
- Ovarian cysts
- Ovarian cancer etc.
There are two kinds of pelvic ultrasound, namely “abdominal” and “vaginal”:
Abdominal pelvic ultrasound
An ultrasound probe is placed on belly to scan pelvic regions. To improve image clarity, women have to keep a full bladder during the scan.
Notes for abdominal pelvic ultrasound:
To help sound waves penetrate bladder during scanning of pelvic organs, women have to drink a large amount of water until there is an urge to urinate 30-60 minutes before ultrasound scan.
Vaginal pelvic ultrasound
Vaginal ultrasound probe is inserted through vagina and placed closer to pelvic organs, it gives clearer images than transabdominal ultrasound. Since the ultrasound probe is inserted into vagina, it is not suitable for women who have no sexual experience.
Notes for vaginal pelvic ultrasound:
- Empty bladder as much as possible before performing vaginal ultrasound
- Not suitable for women who have no sexual experience